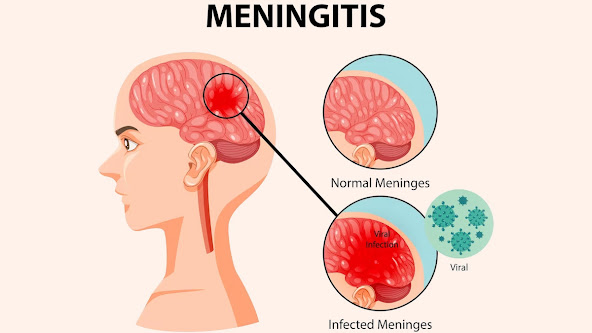
Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes (meninges) surrounding your brain and spinal cord. The swelling from meningitis typically triggers symptoms such as headache, fever, and a stiff neck.
There are different types of meningitis, each caused by different factors:
1. Viral Meningitis: The most common and typically less severe form, caused by viruses.
2. Bacterial Meningitis: More serious and can be life-threatening. It requires immediate medical attention and is caused by various types of bacteria.
3. Fungal Meningitis: Less common and usually affects people with weakened immune systems.
4. Parasitic Meningitis: Rare and can be caused by parasites.
5. Non-Infectious Meningitis: Can be caused by conditions like cancer, lupus, certain drugs, or a head injury.
Early treatment, especially for bacterial meningitis, is crucial to prevent serious complications.
How To Treat and To Prevent Meningitis?
The treatment of meningitis depends on the cause of the infection (bacterial, viral, or fungal) and the severity of the condition.
Here’s a general outline of how meningitis is treated:
1. Bacterial Meningitis.
This is the most serious form and requires urgent medical treatment:
- Antibiotics: Intravenous (IV) antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment. The choice of antibiotic depends on the bacteria causing the infection, which is usually determined by a lumbar puncture (spinal tap).
I highly recommended use DXN FOOD Supplements:
- Corticosteroids: These may be administered to reduce inflammation and swelling around the brain and spinal cord, which can help prevent complications such as hearing loss or brain damage.
- Supportive care: Patients may require fluids, oxygen, and medications to stabilize blood pressure and treat symptoms such as seizures.
2. Viral Meningitis.
Viral meningitis is generally less severe and often resolves on its own, but treatment focuses on relieving symptoms:
- Rest and fluids: Most cases of viral meningitis improve with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to manage headaches and fever.
- Antiviral medications: These are sometimes used if the meningitis is caused by certain viruses, such as herpes simplex virus or varicella-zoster virus.
- Hospitalization: In some cases, particularly in young children, the elderly, or those with weakened immune systems, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor and manage symptoms.
3. Fungal Meningitis
Fungal meningitis is treated with antifungal medications:
- Antifungal drugs: These are administered intravenously, and the treatment can be prolonged, often lasting weeks or months. Common antifungals used include amphotericin B and flucytosine.
- Supportive care: Patients may also require supportive care to manage symptoms and maintain hydration and electrolyte balance.
4. Other Considerations.
- Hospitalization: Many cases of meningitis, particularly bacterial and severe viral cases, require hospitalization to monitor for complications and provide intensive care.
- Treatment of complications: Meningitis can lead to complications like brain damage, hearing loss, and seizures, which require specialized treatments and rehabilitation.
- Prevention: Vaccination is key in preventing certain types of bacterial meningitis, such as those caused by "Neisseria meningitidis", "Streptococcus pneumoniae", and Haemophilus influenzae type b.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
Meningitis is a medical emergency. If you suspect someone has meningitis, especially with symptoms like a severe headache, stiff neck, fever, and sensitivity to light, seek immediate medical attention.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for the best possible outcome.
USE Nutritional & Natural Organic Products like:

No comments:
Post a Comment